> Assays per cell type > Human Mesenchymal Stromal Cells (hMSCs)
Which Quality Control Assays for Human Mesenchymal Stromal Cells (hMSCs)
Human Mesenchymal Stromal Cells (hMSCs) have wide-ranging therapeutic applications but require robust quality control in order to ensure reproducibility of research or a quality end product. Challenges like genomic instability, cell line cross-contamination or mycoplasma need to be addressed effectively.
Stem Genomics recognizes the variety of needs coming from MSC laboratories. We have therefore designed a broad offer for hMSC scientists that takes into account varying budget, performance and timescale expectations.
Discover a wide range of essential quality control assays for hMSCs
Detect over 80% of recurrent abnormalities in hMSCs in record-breaking time !
A G-Banding karyotype service optimized for MSCs
Look deeper into any human cell type and detect targeted SNVs and Indels
Combine 3 essential tests and get results in just 3 days.
Ensure consistent cell line identity throughout your culture
Confidently detect mycoplasma in any human cell culture
Not sure which test could best meet your needs? We’re here to help.
Genomic stability
Genomic stability in MSCs can be altered during their time in culture, raising issues. It can significantly reduce the cells’ differentiation potential, or have a detrimental impact on their therapeutic properties. It can also potentially impact patient safety in the long term (Neri, 2019).
G-Banding karyotyping is the gold standard for detecting abnormalities in mesenchymal stromal cells and provides a comprehensive assessment (balanced and unbalanced translocations, deletions, insertions and inversions).
However, if you need a faster solution at a lower cost, digital PCR can be an interesting alternative.
Finally, if you want to go further in genomic stability testing, a more comprehensive approach including both SNV and CNV detection is required that only the latest sequencing technologies such as NGS (Next Generation Sequencing) can deliver. This powerful technology will allow the detection of SNVs in 361 targeted locations and CNVs across the genome that may not have been previously considered or that could harbor unexpected variations. This comprehensive and unbiased view adds significant information on the genomic stability of your cells.
A range of 3 possible genomic tests to meet your needs:
Detect over 80% of recurrent abnormalities in hMSCs in record-breaking time !
A G-Banding karyotype service optimized for MSCs
Look deeper into any human cell type and detect targeted SNVs and Indels
Cell line authentication
Mislabeling or cross-contamination create risks of misidentification of cell lines. This happens more often than one might think: The International Cell Line Authentication Committee (ICLAC) keeps a registry of misidentified cell lines and to date, estimates that as many as 1/5 to 1/3 of known cell lines are wrongly identified. As of April 2024, their register of Misidentified Cell Lines holds records of 545 misidentified cell lines with no known authentic stock. It is therefore critical to check the cell line identity regularly throughout the time in culture. In terms of methodology, STR has been formally developed into an internationally recognized and accepted consensus standard for human cell line authentication and is the approach recommended by the ISSCR.
Need more information on cell authentication? We’re here to help.
Mycoplasma
Mycoplasma contamination can alter the capacity of pluripotent stem cells to differentiate properly and wreak havoc in labs. Unlike other bacteria, mycoplasma cannot be seen by observation only and can take months to get rid of. It is therefore strongly recommended to regularly check for possible contamination and ensure the complete absence of mycoplasma in your cell culture.
Need more information on mycoplasma testing? We’re here to help.
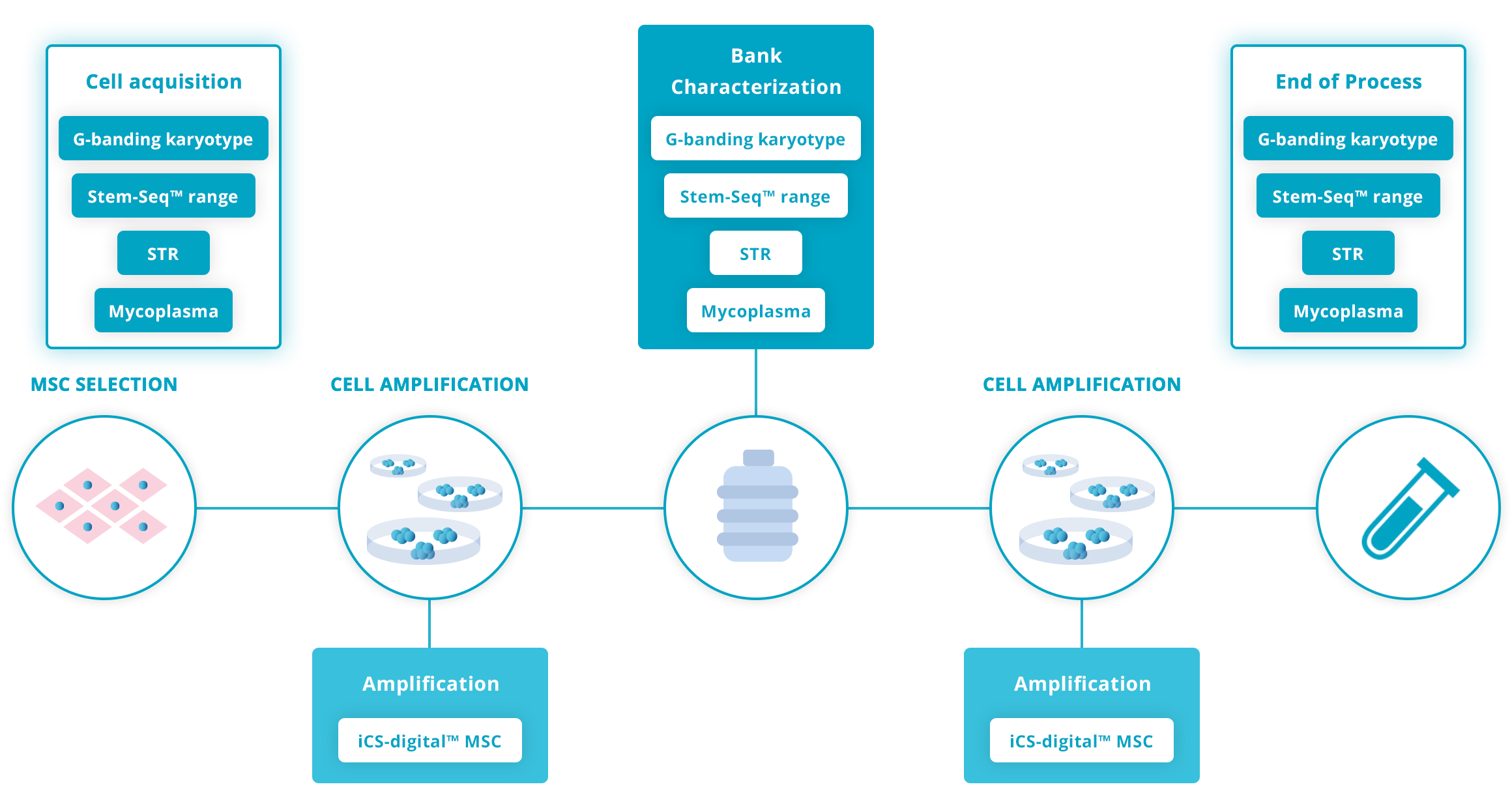
Recommended testing guidelines
The following guidelines are based on our extensive experience working with hMSC research scientists and recognized guidelines such as the ISSCR Standards for Human Stem Cell use in Research.
Click on the graph below for more details
Amplification
Amplification
Definition
Mesenchymal Stromal Cells (MSCs) are multipotent progenitor cells possessing self-renewal ability (limited in vitro) and differentiation potential into mesenchymal lineages, according to the International Society for Cell and Gene Therapy (ISCT).
They are also known as stromal/stem cells, medicinal signalling cells or in relation with their source, for instance “adipose-derived regenerative cells”.
History
In the 1960s, Friedenstein et al. identified a population of fibroblast-like cells that formed clonal colonies in vitro (CFU-F, Colony Forming Unit-Fibroblast) Friedenstein’s observations allowed for the discovery of a specific type of cell, currently referred to as mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). MSCs are primary, non-specialized, non-hematopoietic, plastic-adherent cells with great proliferation potential and the capacity for self-renewal and differentiation. Source: Musiał-Wysocka A, Kot M, Majka M. The Pros and Cons of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Based Therapies. Cell Transplant. 2019 Jul.
List of Stem Genomics' recommended assays for Mesenchymal Stromal Cell:
- iCS-digital™ MSC range: available in 24 probes, this unique test enables up to 80% detection of the most frequent genomic abnormalities in human mesenchymal stromal cells (hMSCs) in 3 days’ turnaround time. Available as a service only. More on iCS-digital™ MSC
- G-Banding: the reference test giving you the structural rearrangement analysis including balanced and unbalanced translocations, deletions, insertions and inversions. Available as a service only. More on G-Banding
- The Stem-Seq™ range: a high-resolution, highly-sensitive, targeted NGS panel specifically designed for SNV and Indel detection combined with a pangenomic view of CNVs. This comprehensive test comes with various levels of reports and interpretations about the significant identified variants. More on the Stem-Seq™ range
- Cell line authentication: easy, fast and affordable STR-based cell line authentication service in just 3 business days. More on the STR service
- Mycoplasma detection: a robust detection method meeting the recommended regulatory guidance of 10 CFU/mL for 60 mycoplasma species. Results in just 3 days. More on Myco-digital.
- One-stop shop: perform 3 essential quality tests in just 3 days! Digital karyotyping, cell authentication and mycoplasma testing from one sample. Also possible to include G-Banding or Pluripotency with extended lead times. Benefit from bulk savings! More on the One-stop-shop service

